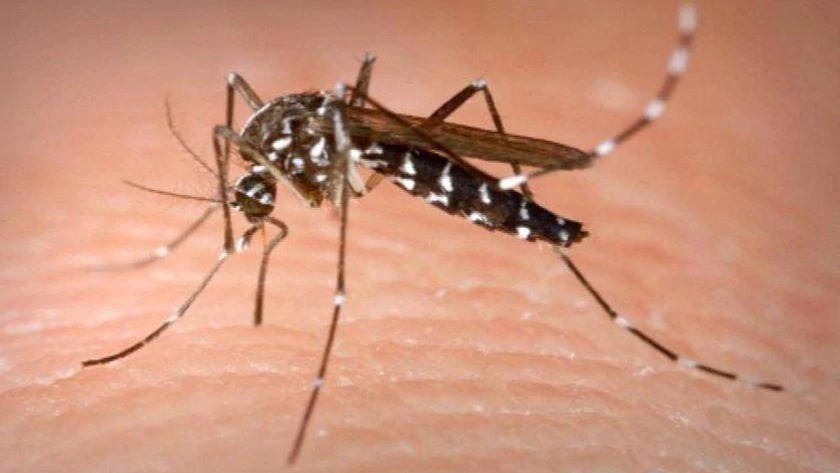
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) has recently been declared a Communicable Disease Incident of National Significance. JEV is a rare but potentially serious infection that can be spread to humans and animals by mosquitoes. The virus cannot be transmitted between humans and cannot be caught by eating pork products.
Current areas of concern in Victoria include: Greater Bendigo, Campaspe, Loddon, Gannawarra, Greater Shepparton, Wangaratta and Indigo local government areas.
Less than one per cent of people infected with JEV will experience symptoms. Illness usually begins with symptoms such as:
- sudden onset of fever
- headache
- vomiting.
If you believe you may be infected with the Japanese encephalitis virus, seek urgent medical assistance.
You can take steps to help prevent mosquito bites:
- Wear light, loose-fitting long-sleeved shirts, long pants and covered footwear and socks (to reduce skin exposure). There are insecticides (e.g. permethrin) available for treating clothing for those spending extended periods outdoors.
- Apply repellent to all areas of exposed skin, especially those that contain DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus which are the most effective against mosquitoes. The strength of a repellent determines the duration of protection with the higher concentrations providing longer periods of protection. Always check the label for reapplication times.
- Reapply repellent after swimming. The duration of protection from repellent is also reduced with perspiration, such as during strenuous activity or hot weather so it may need to be reapplied more frequently.
- Apply the sunscreen first and then apply the repellent. Be aware that DEET-containing repellents may decrease the sun protection factor (SPF) of sunscreens so you may need to re-apply the sunscreen more frequently.
- For children in particular – most skin repellents are safe for use on children aged 3 months and older when used according to directions, although some formulations are only recommended for children aged 12 months and older – always check the product. Infants aged less than 3 months can be protected from mosquitoes by using an infant carrier draped with mosquito netting that is secured along the edges.
For more information, go to https://www.health.gov.au/health-topics/japanese-encephalitis